Describe the Microbial Properties of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
It cannot be seen with the naked eye. Most TB cases are caused by M.
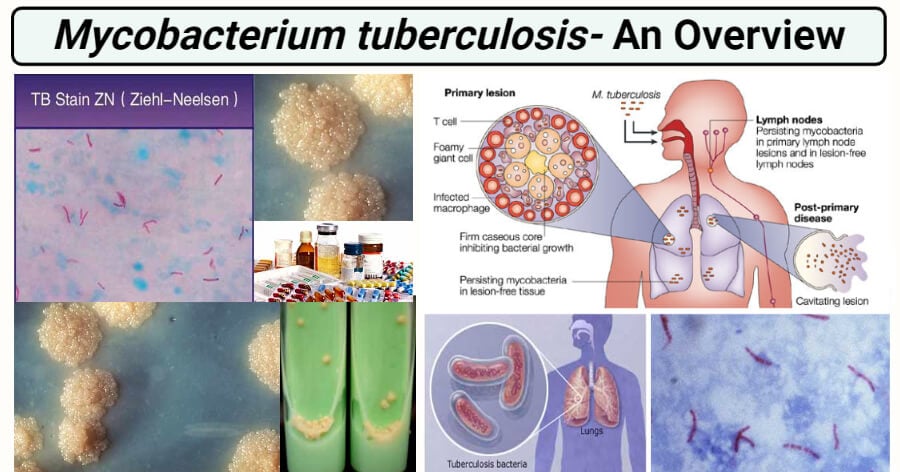
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a acid fast bacteria which can form acid-stable complexes when certain arylmethane dyes are added.

. Cases due to other species are far less prevalent. Mycobacterium comprises acid-fast bacilli ie. And intrinsic drug resistance and antibiotic tolerance.
Tb is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. Organisms are also called tubercle bacilli. One needs a microscope to detect it.
The ability to enter non-replicating states for long periods and cause latent infection. Its cell wall contains several complex lipids long-chain fatty acids called mycolic acids. The high concentration of lipids in the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have been associated with these properties of the bacterium.
It has several notable features. Mycobacterium tuberculosis grows slowly. Clinical sample is cultured in selective broth culture.
There are other bacteria that reproduce every 20 minutes. Tuberculosis W cluster strains the authors carried out in vitro ex vivo and in vivo experiments on 18 clinical strains and 2 laboratory ones which had been clustered by a standardized methodology. Acid-fast bacilli neither gram ve nor gram ve.
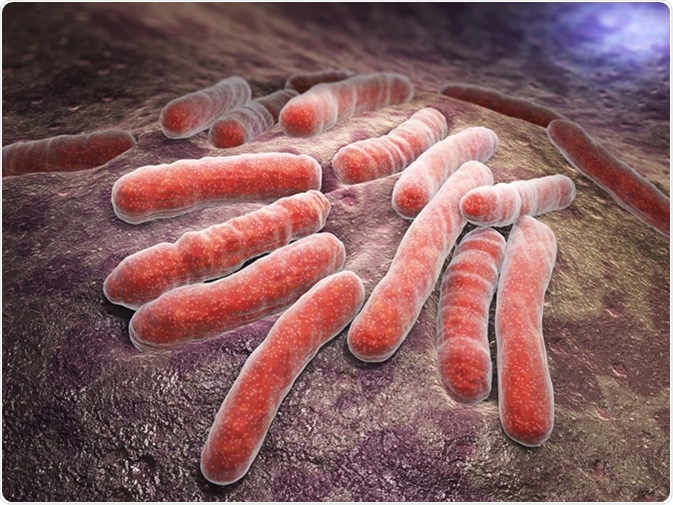
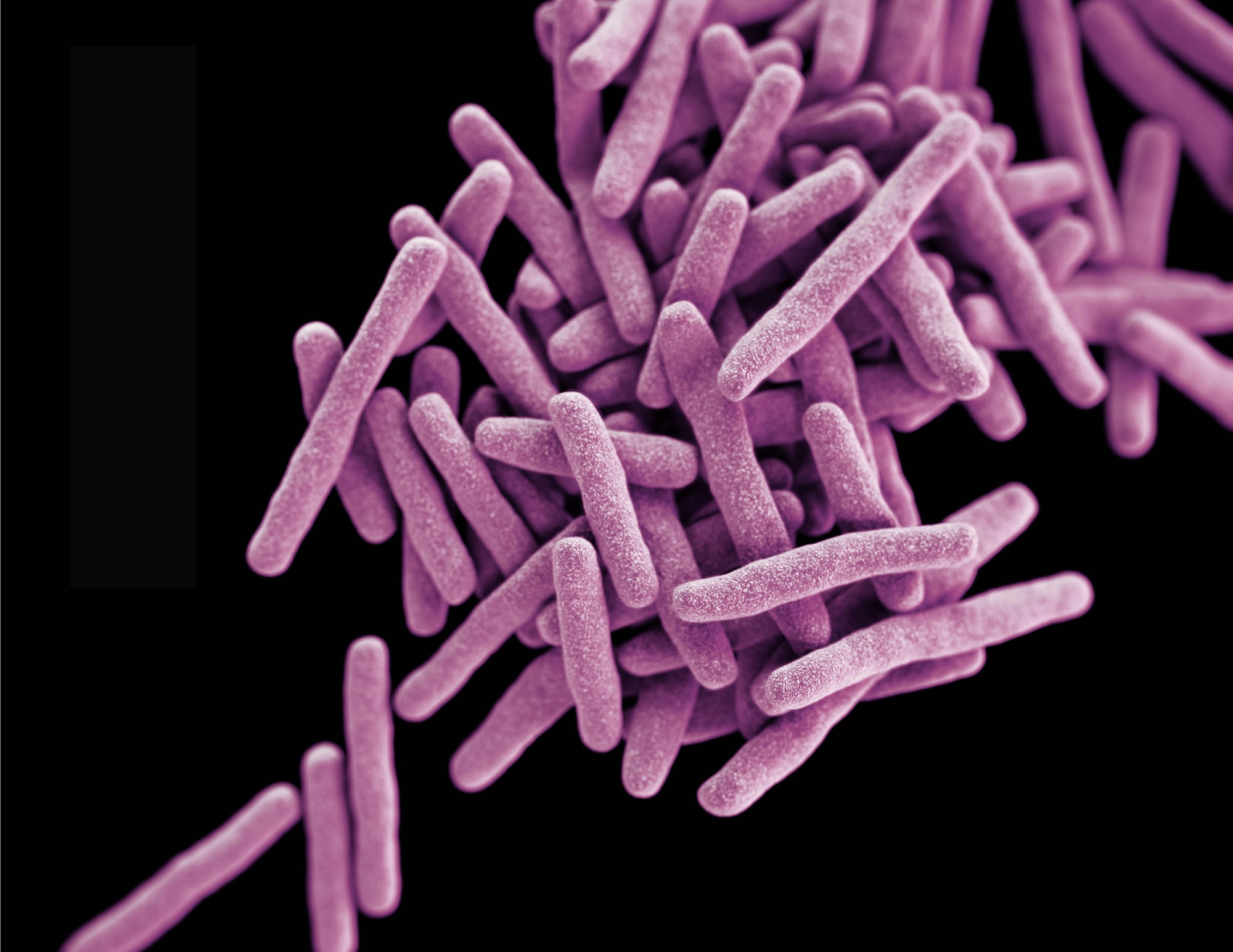
Non-sporing non-motile non-capsulated bacteria. Straight or slightly curved thin rod-shaped bacilli. This bacterium is difficult to staining but once stained it becomes resistant to decolorization by diluted mineral acids this is the reason why Mycobacterium tuberculosis is called Acid Fast bacilli AFB.
TB is caused by members of the specie Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex MTBC which includes. Mycobacteria is an obligate aerobe growing most successfully in tissues with a high oxygen contentthe upper lobe of the lung and the kidney. Description and significance.
The name mycobacterium is derived from the word mold meaning fungus like bacterium. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an acid fast bacteria which can form acid-stable complexes when certain arylmethane dyes are added. This is extremely slow for bacteria.
Long chain fatty acid 60-90 carbons Thick hydrophobic layer in mycobacterium cell wall. Sputum smear is stained with Ziehl-Neelsen stain or fluorescence antibody stain. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an expert and deadly pathogen causing the disease tuberculosis TB in humans.
Morphology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 1. 4 All species of mycobacteria have ropelike structures of peptidoglycan that are arranged in such a way to give them properties of an acid fast bacteria.
They measure 05 µm x 3 µm. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mtb the etiologic agent of TB in humans. The structure of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis when viewed under the microscope shows slender rods this is why they are called Bacilli rods.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch M. All species of mycobacteria have ropelike structures of peptidoglycan that are arranged in such a. Mycobacterium tuberculosis The bacterium that causes tuberculosis.
In the United States the majority of TB cases are caused by. They are known for their ability to lay dormant for decades surviving harsh conditions and treatment with antibiotics. Thin straight rods-04x 3m.
Comparison was made in experiments in. It reproduces itself every 24 to 48 hours. Specifically the Mycobacterium tuberculosis parasitizes blood cells known as macrophages.
This region is responsible for the production of a protein called ESAT-6 that is. MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS Deepshikha Chhetri MSc. List 4 properties of the Mycobacterium cell wall which are beneficial to the bacteria.
A thick waxy cell wall. Pinnipedii causing TB in wild and domesticated mammals. Slow growth rate in culture.
Positive cultures are identified with PCR gene probes specific for M. To study the biological characteristics of M. Tuberculosis has unusually waxy walls is slow-growing and among the most recalcitrant bacteria to treatment.
You use sodium hydroxide to kill all other bacteria and allow TB to grow for 8 weeks. Metabolic remodelling during chronic infection. Like other mycobacteria it is slow growing resulting in more gradual development of disease when compared with other bacterial infections.
Most but not all of these species have been found to cause disease in humans. During acid-fast stain they appear bright red to intensive purple with greenblue background. The bacillus has a rod-shaped body and is approximately 02 millimeter long.
By comparing the genetic sequences of the virulent Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and of the closely-related but non-virulent Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG vaccine strain a region of 9 genes called RD1 is discovered to contribute to the virulence of the bacteria. Impermeability to stains and dyes Resistance to many antibiotics. Mycobacteria are a type of bacteria with thick waxy cell walls.
Microti that causes TB only. Natural resistance to many AMs. It is mesophilic Its average optimum growth temperature is located in the ranges 32 to 37 C.
Tuberculosis has an unusual waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acidThis coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining and as a. Resistant to decolorization by weak mineral acids because they have an unusual cell wall that contains mycolic acid acid instead of NAM and has a very thick high lipid content 60-70. Tuberculosis is a small rod-shaped strictly aerobic acid-fast bacillus 1.
Africanum that causes TB in humans only in certain regions of Africa. TB has many manifestations affecting bone the central nervous system and many other organ systems but it is primarily a pulmonary disease that is initiated by the deposition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis contained in aerosol droplets onto lung alveolar surfaces. On artificial media coccoid and filamentous forms are seen with variable morphology from one species to another.
From this point the progression of the disease can have several outcomes determined largely by the.
Tuberculosis Bacteria Thrive On A Nitrogen Source Buffet Elife Science Digests Elife
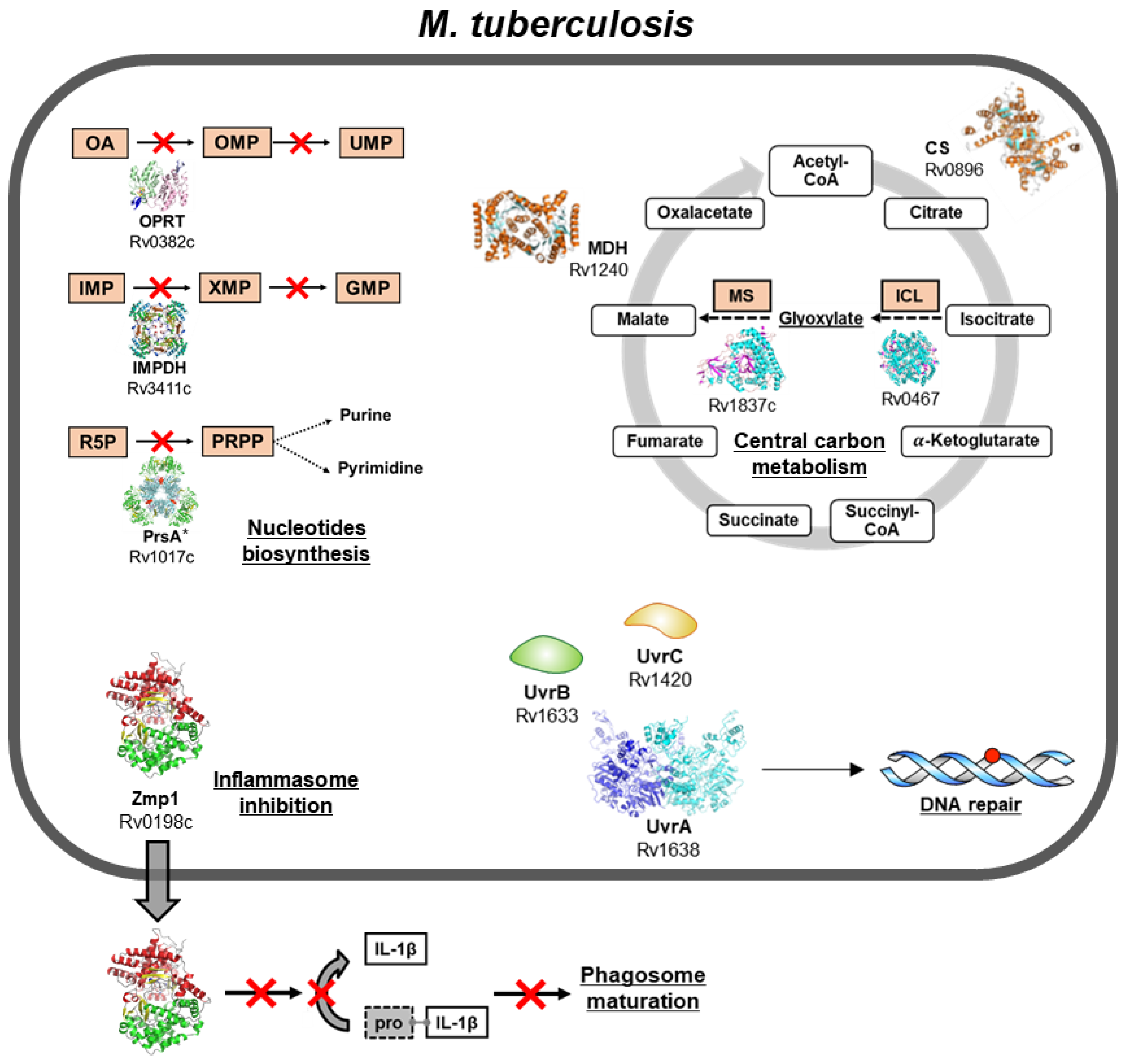
Pathogens Free Full Text Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Molecular Determinants Of Infection Survival Strategies And Vulnerable Targets Html

Recent Developments In The Application Of Flow Cytometry To Advance Our Understanding Of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Physiology And Pathogenesis Parbhoo 2020 Cytometry Part A Wiley Online Library

Recent Developments In The Application Of Flow Cytometry To Advance Our Understanding Of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Physiology And Pathogenesis Parbhoo 2020 Cytometry Part A Wiley Online Library

Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Mtb Lipid Mediated Lysosomal Rewiring In Infected Macrophages Modulates Intracellular Mtb Trafficking And Survival Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Cavitary Tuberculosis The Gateway Of Disease Transmission The Lancet Infectious Diseases
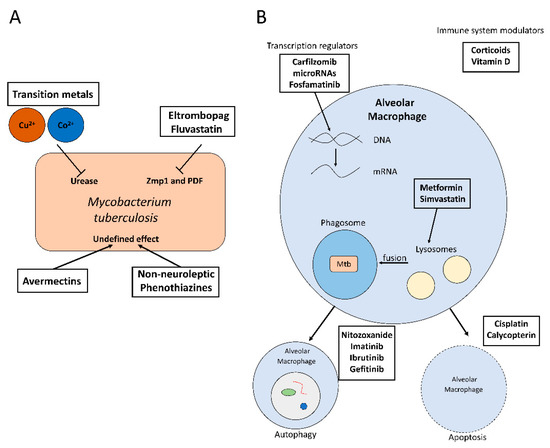
Antibiotics Free Full Text Novel Treatments Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Based On Drug Repurposing Html

Recent Developments In The Application Of Flow Cytometry To Advance Our Understanding Of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Physiology And Pathogenesis Parbhoo 2020 Cytometry Part A Wiley Online Library
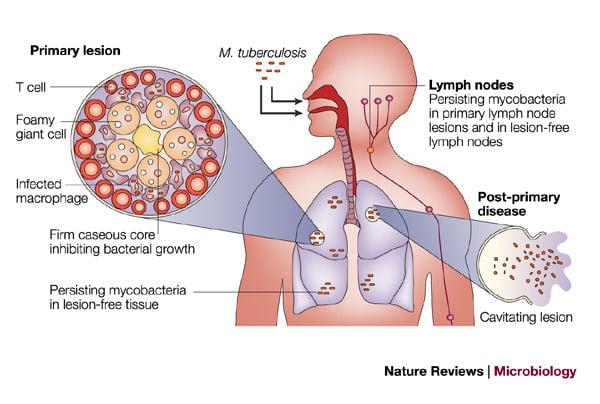
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis An Overview Microbe Notes

978 620 2 67524 6 In 2022 Microbiology Healthcare System Pharmacological
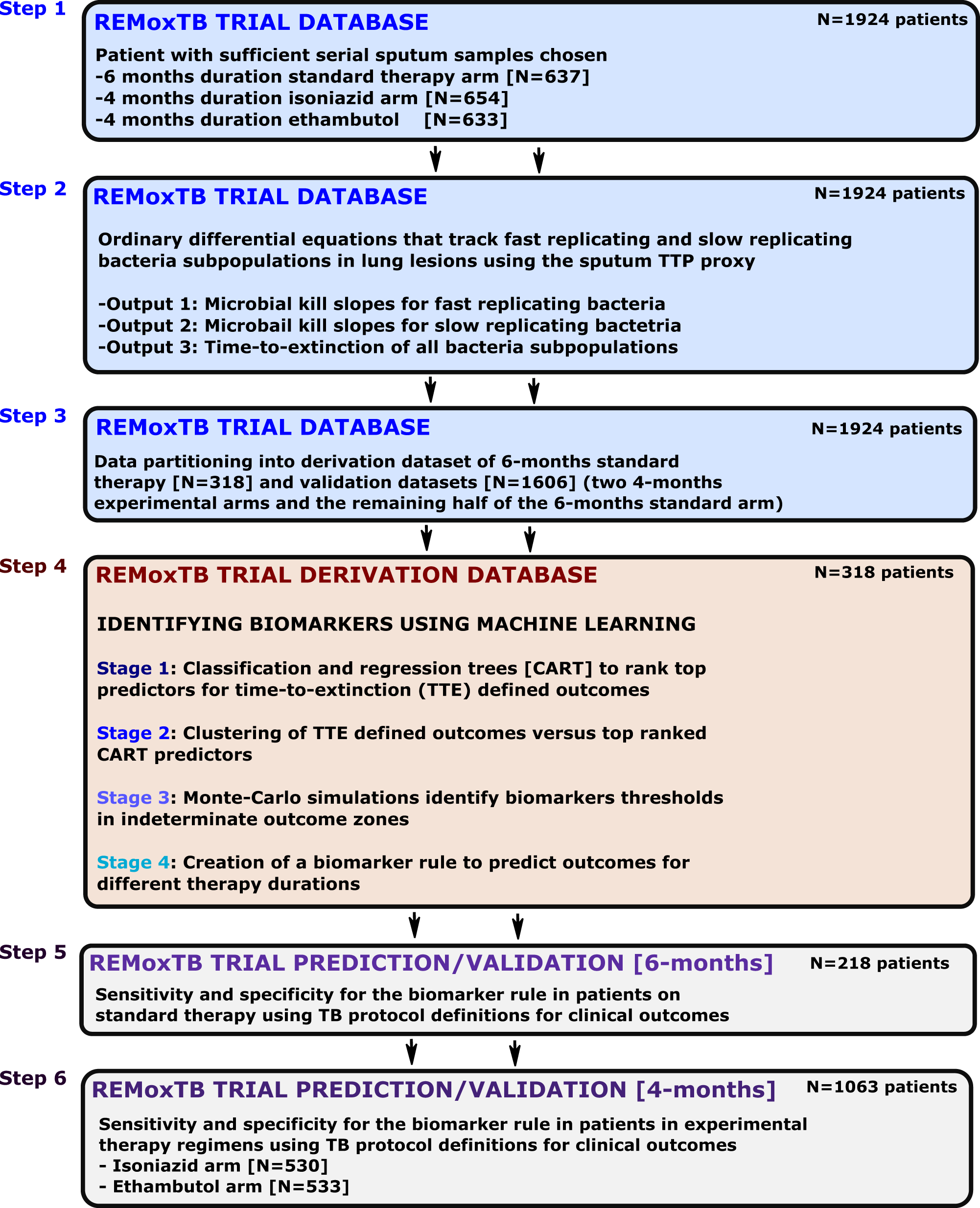
Bacterial Load Slopes Represent Biomarkers Of Tuberculosis Therapy Success Failure And Relapse Communications Biology

Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 14313982 1 Microbiome Probiotics Gut Health

Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Antimicrobials Immunity And Lung Gut Microbiota Crosstalk Current Updates And Emerging Advances Osei Sekyere 2020 Annals Of The New York Academy Of Sciences Wiley Online Library
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Microbiology Society
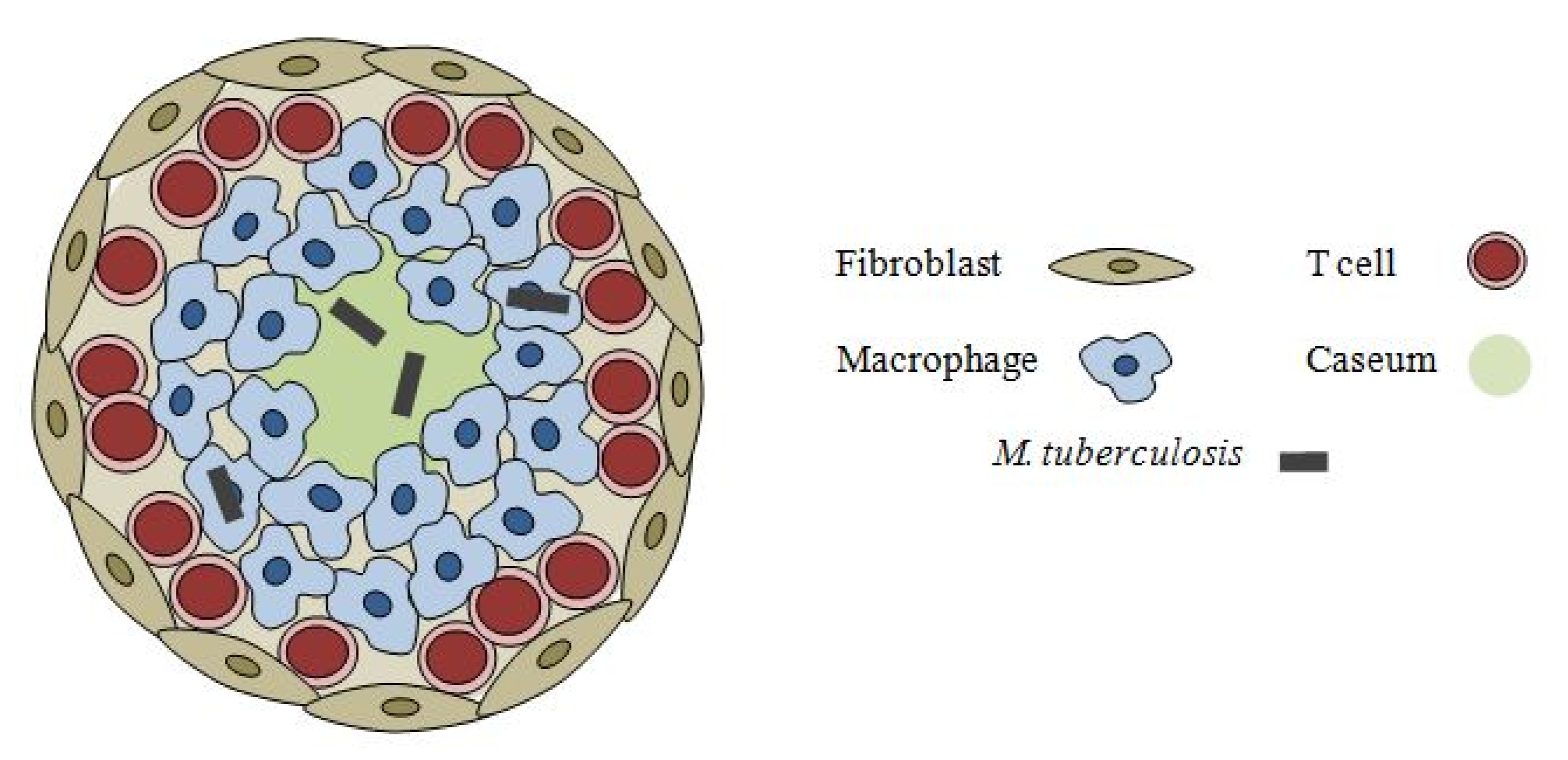
Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text The Role Of Transport Mechanisms In Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Drug Resistance And Tolerance Html
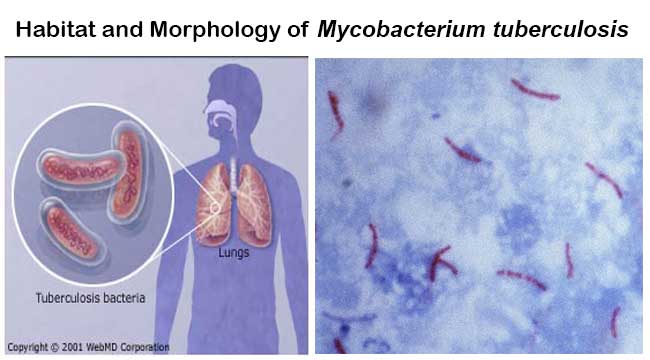
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis An Overview Microbe Notes